History of the Netherlands including a description of the tulip craze

History of the Netherlands including a description of the tulip craze
William Shakespeare biography

Jeffrey Rosen of the National Constitution Center in conversation with Walter Isaacson of the Aspen Institute. Created by Aspen Institute.
Jeffrey Rosen of the National Constitution Center in conversation with Walter Isaacson of the Aspen Institute. Created by Aspen Institute.
By the 1920s, a majority of the US population lived in cities rather than in rural areas. In this video, Kim explores the economic opportunities cities offered to women, migrants, and immigrants, as well as the passage of new immigration restrictions.
In this second video giving an overview of World War II, we see Germany and the Axis powers only continue to gain momentum in 1940.
In 1941, the Axis gains further momentum with control of most of Continential Europe. Hitler decides to break pact and invade Stalin's Soviet Union. United States enters World War II after Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor.
In 1942 we see the Axis get pushed back in North Africa and get bogged down in the Soviet Union. The tide of war turns in favor of the Allies.
In 1943, the tide really turns in favor of the Allies in World War II. They are able to push the Axis out of N.Africa and force a surrender from Italy (along with Mussolini being deposed). The Soviets are able to start pushing the Axis out of the Soviet Union.
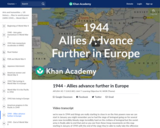
As we go into 1944, we see the allies land at Normandy, liberate France and face Germany in their last major counteroffensive at the Battle of the Bulge. On the Eastern Front, the Soviets end Siege of Leningrad and begin to push through Poland and Romania. In the south, Allies land in southern France and take Rome.
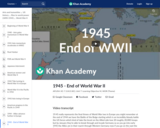
1945 marks the end of World War II. V-E Day (Victory in Europe Day) is May 8th 1945. War doesn't end in the Pacific until August of 1945 with the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
An introductory course using visual materials with emphasis on methods and motivations that generate the visual experience, both past and present. Art practices from around the world are examined for form and content. Emphasis will be on Western Art.
Course Outcomes:
1. Articulate verbally and in writing a general understanding of the significance of visual art in a wide variety of culture and media.
2. Create a personal work of art. Articulate verbally and in writing the form and content of the piece, along with information about significant artists and art works relative to the created artwork, and to visual art.
3. Articulate verbally and in writing appropriate art vocabulary, and art evaluation concepts, when viewing visual art.
Ce livre est un hommage à son travail dont la portée et le caractère précurseur nous sont plus sensibles que jamais, près d’un demi-siècle après la publication de ses articles majeurs. Puissent les jeunes d’Afrique et d’ailleurs être nombreux à suivre son exemple! À noter que les textes présentés ici (à l’exception de l’article de 1969 sur « La conférence de Nairobi » et du cahier photographique) sont aussi publiés dans l’ouvrage que j’ai co-dirigé avec Mamadou Badji Du soleil pour tous. L’énergie solaire au Sénégal : un droit, des droits, une histoire (2018, Éditions science et bien commun).
This textbook covers a variety of topics related to African American History and culture, from African Origins to the Reconstruction era.

African American History and Culture contains 10 modules starting with African Origins - History and Captivity and continuing through Reconstruction. Openly-licensed course materials developed for the Open Educational Resources (OER) Degree Initiative, led by Achieving the Dream https://courses.lumenlearning.com/catalog/achievingthedream.

This course asks students to consider the ways in which social theorists, institutional reformers, and political revolutionaries in the 17th through 19th centuries seized upon insights developed in the natural sciences and mathematics to change themselves and the society in which they lived. Students study trials, art, literature and music to understand developments in Europe and its colonies in these two centuries. Covers works by Newton, Locke, Voltaire, Rousseau, Marx, and Darwin.
This course focuses on the Great Depression and World War II and how they led to a major reordering of American politics and society. We will examine how ordinary people experienced these crises and how those experiences changed their outlook on politics and the world around them.
This class examines how and why twentieth-century Americans came to define the ŰĎgood lifeŰ through consumption, leisure, and material abundance. We will explore how such things as department stores, nationally advertised brand-name goods, mass-produced cars, and suburbs transformed the American economy, society, and politics. The course is organized both thematically and chronologically. Each period deals with a new development in the history of consumer culture. Throughout we explore both celebrations and critiques of mass consumption and abundance.
Environmental History is about looking at the past as if the environment matters. American History is about looking at the past of not only the United States, but of both the American continents. This wider view is especially important when we realize that people occupied the Americas for over 15,000 years before Europeans arrived and that when the came to the Americas, Europeans focused their interest for centuries on areas that are not part of the current United States. As we get closer to the present, we will focus more on the U.S., but we’ll try to remind ourselves from time to time that we’re not the only nation in the Americas by considering how other nations have experienced and affected the environment.
This is a collection of Coursework for an American History course.