This curriculum covers a broad range of economic concepts and models. Students will learn foundational concepts like scarcity, opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and distinguishing between positive and normative claims. Core microeconomic topics include supply and demand, elasticity, market efficiency, consumer/producer surplus, and government intervention. Macroeconomic topics span GDP, unemployment, inflation, business cycles, growth, fiscal policy, monetary policy, and stabilization tools.
The microeconomics section builds an understanding of how individual buyers and sellers interact in markets. Students analyze supply and demand equilibria, surpluses, and shortages. Elasticity concepts are applied to understand how quantity supplied and quantity demanded respond to price changes. Market outcomes are evaluated using consumer/producer surplus and efficiency criteria. The effects of government price controls and taxes are analyzed.
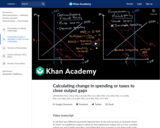
The macroeconomics portion develops models to explain economy-wide outcomes. Students learn to calculate GDP, unemployment rates, inflation, and price indices. The AD-AS model illustrates macro equilibrium and the causes of business cycles, inflation, and stagnation. The Keynesian and Neoclassical frameworks are compared. Fiscal and monetary policies are explored as stabilization tools, with analysis of their mechanisms, limitations, lags, and appropriate applications.
International economics connects micro and macro concepts. Using theories of comparative advantage, students evaluate the impacts of trade and trade policies on consumers, producers, and the macroeconomy. The determinants of exchange rates and trade balances are analyzed.
This curriculum provides both theoretical frameworks and practical applications of economics. Students build analytical and mathematical skills for modeling and evaluating economic outcomes. Policy tradeoffs are examined from multiple perspectives. Upon completion, students will be equipped with core microeconomic and macroeconomic ways of thinking to apply in their careers and lives.