- Subject:
- Life Science, Biology
- Level:
- Academic Lower Division
- Tags:
Unit 3
The Cell
- Cell Structure

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Studying Cells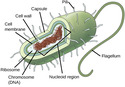
Lesson 3
Prokaryotic Cells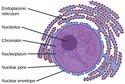
Lesson 4
Eukaryotic Cells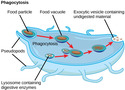

Lesson 6
The Cytoskeleton
- Structure and Function of Plasma Membranes

Lesson 8
Introduction
Lesson 9
Components and Structure
Lesson 10
Passive Transport
Lesson 11
Active Transport
Lesson 12
Bulk Transport
- Metabolism

Lesson 13
Introduction
Lesson 14
Energy and Metabolism
Lesson 16
The Laws of Thermodynamics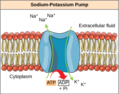
Lesson 17
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate
Lesson 18
Enzymes
- Cellular Respiration

Lesson 19
Introduction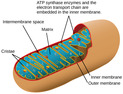
Lesson 20
Energy in Living Systems
Lesson 21
Glycolysis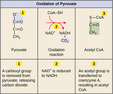
Lesson 23
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Lesson 24
Metabolism without Oxygen
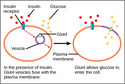
Lesson 26
Regulation of Cellular Respiration
- Photosynthesis
Lesson 27
Introduction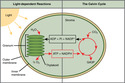
Lesson 28
Overview of Photosynthesis
- Cell Communication

Lesson 31
Introduction
Lesson 33
Propagation of the Signal
Lesson 34
Response to the Signal
Lesson 35
Signaling in Single-Celled Organisms
- Cell Reproduction
Lesson 36
Introduction
Lesson 37
Cell Division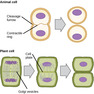
Lesson 38
The Cell Cycle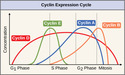
Lesson 39
Control of the Cell Cycle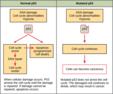
Lesson 40
Cancer and the Cell Cycle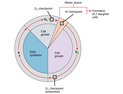
Lesson 41
Prokaryotic Cell Division