- Subject:
- Life Science, Biology
- Level:
- Academic Lower Division
- Tags:
Unit 4
Genetics
- Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction

Lesson 1
Introduction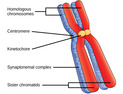
Lesson 2
The Process of Meiosis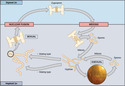
Lesson 3
Sexual Reproduction
- Mendel's Experiments and Heredity

Lesson 4
Introduction
Lesson 6
Characteristics and Traits
Lesson 7
Laws of Inheritance
- Modern Understandings of Inheritance
Lesson 8
Introduction
- DNA Structure and Function

Lesson 11
Introduction

Lesson 13
DNA Structure and Sequencing
Lesson 14
Basics of DNA Replication
Lesson 15
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes
Lesson 16
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
Lesson 17
DNA Repair
- Genes and Proteins

Lesson 18
Introduction
Lesson 19
The Genetic Code
Lesson 20
Prokaryotic Transcription
Lesson 21
Eukaryotic Transcription
Lesson 22
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes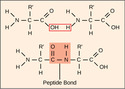
Lesson 23
Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
- Gene Expression
Lesson 24
Introduction
Lesson 25
Regulation of Gene Expression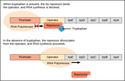
Lesson 26
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation


Lesson 31
Cancer and Gene Regulation
- Biotechnology and Genomics

Lesson 32
Introduction
Lesson 33
Biotechnology
Lesson 34
Mapping Genomes
Lesson 35
Whole-Genome Sequencing
Lesson 36
Applying Genomics
Lesson 37
Genomics and Proteomics