
Price of one good impacting quantity demanded of another. Created by Sal Khan.
- Subject:
- Economics
- Social and Behavioral Sciences
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 08/10/2021

Price of one good impacting quantity demanded of another. Created by Sal Khan.
To get a better intuition about how much a consumer values a good in a market, we think of demand as a marginal benefit curve. In this video we look at the demand curve from a marginal benefit framework. Created by Sal Khan.
How to account for things when you own the building instead of renting it. Created by Sal Khan.
Where does a buyer's demand curve come from? A rational buyer wants to get as much "bang per buck" from their consumption as possible. In economics, that's called marginal utility per dollar spent. When the price of a good decreases, the "bang per buck" on that good increases, which incentivizes consuming more of it. In this video, we derive the individual's demand curve for a good by tweaking the marginal utility per dollar spent. Created by Sal Khan.
Walk through the logic of determining what kind of good has the most elastic demand in this video.

There are several factors that affect how elastic (or inelastic) the price elasticity of demand is, such as the availability of substitutes, the timeframe, the share of income, whether a good is a luxury vs. a necessity, and how narrowly the market is defined. We explore each of these in this video.
This course introduces the theory of relative prices in a market system, consumer choice, marginal analysis, and the allocation of productive resources among alternative uses in a market economy. Other topics may include market power and price discrimination, public finance, the labor market and environmental policy.
Course Outcomes:
1. Discuss the role scarcity plays in defining economic choices and how individuals, companies and nations resolve these issues.
2. Describe and apply marginal principle, principle of opportunity cost, principle of diminishing returns, comparative advantage, and elasticity.
3. Analyze the relationships between production costs and cost curves.
4. Explain the mechanics of supply and demand and apply the supply and demand model to evaluate markets.
5. Discuss the efficiency and equity of both competitive and noncompetitive markets and how both are impacted by government intervention.
6. Explain, compare and contrast, and apply in context each of the basic market structures - i.e. perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly and monopolistic competition.

Test and Question Bank for OpenStax Course ECON.2312 Microeconomics in Word and TestGen format.

15.010 is the Sloan School's core subject in microeconomics, with sections for non-Sloan students labeled 15.011. Our objective is to give you a working knowledge of the analytical tools that bear most directly on the economic decisions firms must regularly make. We will emphasize market structure and industrial performance, including the strategic interaction of firms. We will examine the behavior of individual markets--and the producers and consumers that sell and buy in those markets--in some detail, focusing on cost analysis, the determinants of market demand, pricing strategy, market power, and the implications of government regulatory policies. We will also examine the implications of economics on other business practices, such as incentive plans, auctions, and transfer pricing.

Economic models are a way of taking complicated ideas and events and breaking them down into their most important characteristics. We use models in economics so that we can focus our attention on a few things instead of getting bogged down a lot of details. In this video, learn more about the role that models play in economics, and the importance of the assumptions that underlie those models.
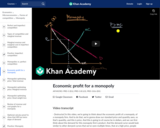
Learn about how to represent a monopoly market graphically in this video. Topics covered include the profit-maximizing quantity, pricing decisions, and deadweight loss associated with monopolies.

An important skill in microeconomics is the ability to find a firm's profit. Learn more about how to use a graph to identify the profit-maximizing quantity for a firm in a perfectly competitive market, and identify the area that represents the firm's profit or loss.
Accounting profit is what many people tend to think of when they think profit, but an economist would say that you leave something very important out when you do so: opportunity costs. In this video, explore the difference between a firm's accounting and economic profit. Created by Sal Khan.
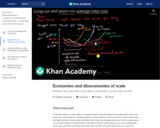
Economies of scale exist when long run average total cost decreases as output increases, diseconomies of scale occur when long run average total cost increases as output increases, and constant returns to scale occur when costs do not change as output increases.
Why we calculate percent changes in a strange way when calculating elasticities. Created by Sal Khan.
Thinking about elasticity of supply. Created by Sal Khan.
Total surplus is maximized in a market at equilibrium. In this video, we talk about why this is and the math behind this assertion.

Tax incidence is a description of how the burden of a tax falls in a market. In this video we break down how to identify consumer surplus, producer surplus, tax revenue and tax incidence, and dead weight loss after a tax.

In this video, learn how to apply the analysis of factor markets to a sample problem.
Price changes the quantity supplied, but what might cause supply to increase even if price hasn't changed? In this video, we explore the determinants of supply: those factors that cause an entire supply curve to shift. Created by Sal Khan.